According to statistics, up to 20% of the population suffers from varicose veins of the lower extremities, while in women the disease appears 2 times more often. It has been proven that women have additional predisposing factors that contribute to a decrease in vascular tone (pregnancy, taking estrogen-progestogen contraceptives, imbalance of sex hormones).The types of treatment for leg veins do not differ between men and women, however, the frequency of postoperative relapses in women is higher due to the additional influence of hormones (estrogen and progesterone influence).
What causes varicose veins in women's legs?
Venous diseases of the legs should be treated by a phlebologist who deals specifically with this pathology. Various methods of treating varicose veins are not radical, as they are not aimed at eliminating the main pathogenic cause - the failure of the venous valve apparatus. Surgical and conservative treatment delay the progression of the disease for long periods. The recurrence rate is high and reaches from 10 to 50% 5 years after surgery.
Treatment of varicose veins should be comprehensive. There are three groups of methods for eliminating varicose veins:
- phlebosclerosing,
- surgical,
- conservative.
Each type of treatment has its own advantages and disadvantages and a certain rate of return. The choice of method is conditional, as the phlebologist often has to combine all three methods to achieve the most favorable result.
Characteristic symptoms of varicose veins in women
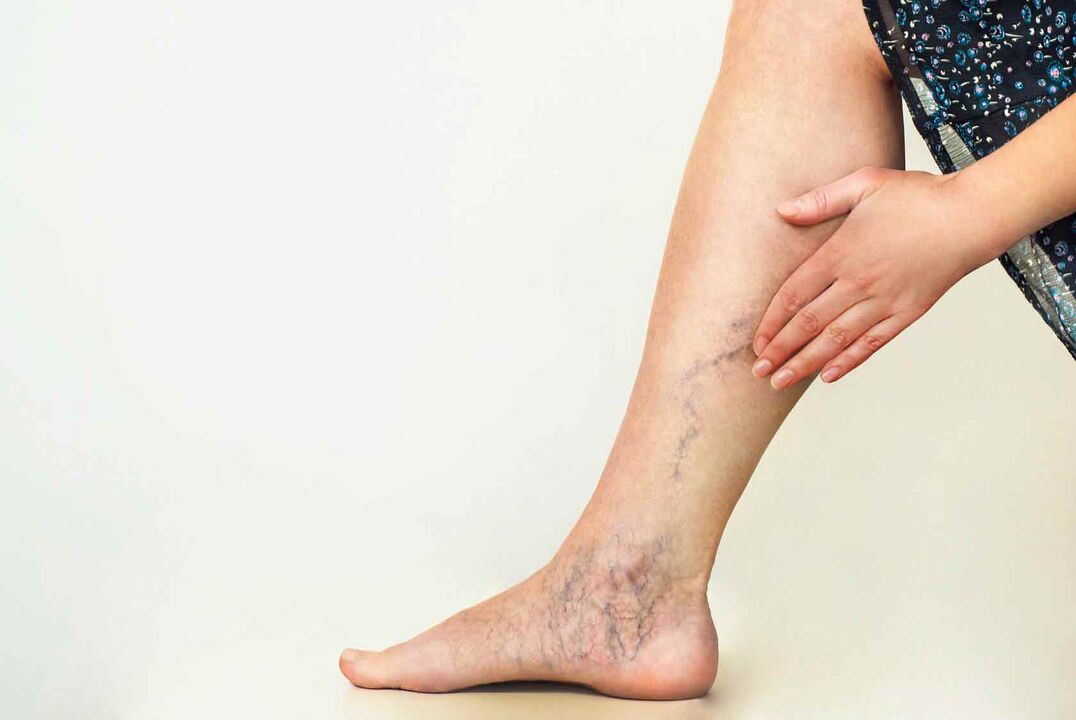
Symptoms of varicose veins begin with the appearance of such functional disorders as a feeling of heaviness in the legs, swelling of the ankle joints at the end of the working day. Spider veins first form on the skin of the legs.
Spider veins are one of the first symptoms of developing varicose veins in the legs. The main signs of the disease - associations of varicose saphenous veins - appear several years after the onset of the disease. If not treated at this stage, symptoms such as cramps in the calf muscles and itchy skin on the legs appear.
Signs of trophic disorders: pigmentation of the skin in the lower third of the leg, cyanosis, sclerotic changes in the subcutaneous tissue, eczema, against which a trophic ulcer is formed.
Characteristic symptoms of varicose veins in women
- Painful symptoms appear cyclically and intensify before menstruation, which are accompanied by changes in the level of sex hormones;
- During pregnancy, the signs of varicose veins may disappear after delivery;
- in the second half of the menstrual cycle, due to the action of progesterone, the diameter of the varicose veins increases, so the symptoms of swelling and heaviness in the legs are more pronounced;
- signs of varicose veins worsen during hormone therapy.
Now let's talk about therapy methods.
Radiofrequency ablation and endovenous laser coagulation
Radiofrequency ablation of veins
The method is based on the introduction, under ultrasound guidance, of a special available catheter into the lumen of the dilated vein. The catheter is equipped with a special electrode, the working part of which is heated to 120 degrees under the influence of radio frequency radiation. Advancing the catheter along the vein leads to adhesion or "welding" of the vascular wall. Obliterated veins are excluded from the circulatory system of the legs.
Endovenous laser coagulation
The surgical technique consists of drilling the affected vein and inserting a laser light guide into its lumen under ultrasound control. Under the influence of laser radiation, the proteins of the blood vessel wall coagulate, as a result of which the vein collapses and after some time is covered with connective tissue. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and endovenous laser ablation (EVLO) are relatively new methods for treating varicose veins in the legs. Despite the differences in execution techniques, they have common characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of RFA and EVLA
| It does not require hospitalization | High price |
| Execution speed (from 30 minutes to 1 hour) | Return rate up to 10% |
| Without pain | Impossibility of performing the procedure due to some anatomical features of the veins (severe twisting of blood vessels) |
| No blood | |
| It is performed under local anesthesia | |
| Lack of postoperative scarring (desirable cosmetic effect for women) | |
| Short rehabilitation periods |
RFA or EVLO is chosen by women who want to treat varicose veins on an outpatient basis with minimal restriction of physical activity in the postoperative period and maintaining the aesthetic appearance of their legs.
Phlebosclerotherapy
A special drug is injected into the lumen of the affected segment of the vein, which has a sclerosing ("adhesive") effect on the vascular wall. The sclerosing agent can be used in liquid or foam form. Preference should be given to foam sclerotherapy due to the greater contact area of the substance with the vein wall.
Advantages and disadvantages of phlebosclerotherapy:
| There is no postoperative scar | Possible long-term pigmentation of the skin at the piercing site (up to 2 years) |
| It is performed on an outpatient basis | In rare cases, inflammation of the vein after surgery (phlebitis) |
| The operation is performed without anesthesia | Swelling and redness of the tissues for 2 days after the procedure |
| Manipulation is practically painless (slight burning at the puncture site) | Allergic reaction due to individual intolerance to the drug |
| In 20% of cases, spider veins appear on the legs (telangiectasia) | |
| Up to 50% recovery rate |
The recurrence of varicose veins after sclerotherapy depends on the lumen of the affected vessel - the wider the lumen, the higher the risk of recanalization in it. Sclerosis therapy is chosen in the treatment of recurrent varicose veins after surgical phlebectomy.
Surgical phlebectomy
Surgery is a more radical way to eliminate varicose veins. The principles of surgical treatment are the elimination of the pathological discharge of blood from the deep to superficial veins of the legs and the removal of the dilated vessels themselves. Stages of combined phlebectomy:
- Crossing and ligation of the mouth of the great saphenous vein (incision in the groin area) or the small saphenous vein (incision in the popliteal fossa);
- Removal of trunks of varicose veins. It is performed using a special metal probe that pulls the vein into the skin incision.
| Radicality | Hospitalization from 5 to 7 days |
| The possibility of performing the operation at any stage of the disease | Leg wound |
| Spinal or general anesthesia | |
| Injury to surrounding tissue when a vein is pulled | |
| Possible complications: bleeding, wound infection | |
| Return rate up to 20% |
Surgical treatment is preferred for the type of trunk lesion, when the varicose deformation of the great or small saphenous veins occurs to a significant extent. And also when there are signs of soft tissue trophic disorders and symptoms of venous insufficiency decompensation.
Miniphlebectomy
Miniphlebectomy is a special surgical option that can treat varicose veins of the legs in the initial stages. It is most often used in the presence of single varicose veins on the legs. A puncture is made in the skin above the pathological formation and the vein is pulled and crossed using a hook. The operation does not require general anesthesia or skin sutures.
Conservative therapy
It is necessary to start the treatment of varicose veins in the legs with the use of medication and compression therapy.The prescription of medications that improve blood circulation and the wearing of medical compression stockings are the main conditions that determine the outcome of any surgical intervention in the veins of the legs.
Compression therapy
Elastic leg compression is the main method of treatment in cases where surgery is contraindicated. Elastic bandages and special medical knitwear can be used as compression products: socks, knee socks, tights. Medical products are very durable, maintain the original level of compression for a long time and are comfortable to wear, which is important for women.
There are 4 classes of elastic knitwear depending on the degree of compression. It is recommended to treat varicose veins using class 2 products in the absence of disease progression for up to 6 months and with further use during physical activity or prolonged standing. If there are signs of damage to the valves of the deep veins or severe symptoms of impaired lymphatic drainage, then class 3 valves are prescribed until the progression of the varicose veins stops.
The therapeutic effect of compression stockings is due to:
- a decrease in the volume of the vein, which leads to less blood discharge in the varicose vessels;
- increased absorption of tissue fluids into the bloodstream, due to which signs of swelling and symptoms of heaviness in the legs disappear;
- improving blood circulation, which prevents the formation of blood clots.
Varicose veins are one of the oldest diseases known to mankind. Mentions of it are found in the works of Avicenna, Hippocrates, Paracelsus and other legendary healers, and the Italian scientist Marcello Malpighi devoted many years to his study. The pathology can affect any organ where there are large veins (stomach, esophagus, male testicles), but varicose veins of the lower extremities are the most common. Let's talk about the causes of varicose veins in the legs, methods of diagnosis and elimination.
About varicose veins of the lower extremities
Varicose veins are an irreversible expansion of the veins due to the breakdown of the valves involved in the circulation mechanism of the veins of the lower extremities. With normal muscle contraction and relaxation, it moves strongly upward from valve to valve, but when the vein expandsthe valves stop closing and blood flow slows, which leads to a variety of clinical symptoms.
According to statistics, people today suffer from the symptoms of varicose veins in the legs:every tenth man and every third woman aged 30-40. Among the main countries in terms of pathology prevalence are the developed countries of Europe, where it is diagnosed in 30-40% of the population; Varicose veins are less common in Africa and Asia (about 0. 1%).
Why it appears, risk factors
The exact causes of the disease are not known, but most expertsleans toward the hereditary theory: people who have had cases of varicose veins in their family are at risk. Factors that provoke the development of pathology also include:
- geNDer. Women are more susceptible to varicose veins than men - this is due to increased venous load during pregnancy and childbirth, as well as taking hormonal drugs;
- bad habits and excess weight. Smoking, abuse of fatty foods and alcohol have a negative impact on blood circulation in the body, increase the load on the veins and can cause related disorders;
- Work conditions. People who, due to the nature of their profession, are forced to stand or sit motionless for a long time (hairdressers, salesmen, waiters, office workers) suffer from this disease more often than others;
- excessive physical activity. Another category of people who are at risk of developing varicose veins are those who engage in heavy physical work or certain strength sports (for example, lifting weights);
- uncomfortable clothes or shoes. Tight, restrictive clothing and high-heeled shoes also contribute to the deterioration of venous blood circulation.
Distribution
Most often (in 75-80% of cases) the disease affects the trunk and branches of the great saphenous vein, in 5-10% - the small saphenous vein, and in 7-10% of patients both veins are involved in the process. . In the clinical course of varicose veins of the lower extremities, experts distinguish two forms and four groups.
Form:
- descending– the process spreads from top to bottom along the great femoral vein, starting from its mouth;
- going up– the disease begins in the legs and is caused by a malfunction of the valve apparatus of the deep veins.
Groups:
- subcutaneous or intradermal pathology not burdened by venous discharge;
- segmental with reflux through perforating and superficial veins;
- diffuse with venous reflux (through superficial and perforating veins);
- dilatation with reflux through the deep veins.
According to the degree of venous insufficiency, four main stages of varicose veins are distinguished:
- - the symptoms of the disease may be present, but it is not determined by diagnostic methods;
- I - this stage is characterized by transient swelling, the syndrome of "heavy legs" and the appearance of "spider veins";
- II - the appearance of constant swelling that appears in the evening, skin discoloration, eczema;
- III - the presence of trophic ulcers, including non-healing ones.
Risk and complications
The risk to the patient's health and life does not come from the disease itself, but from the complications it causes. These include damaged skin nutrition, which causesTrophic ulcers and erysipelas may form, as well as the most dangerous complication – thrombophlebitis. It leads to increased thrombus formation, as a result of which blood clots, being detached from the venous walls, can disrupt the functioning of internal organs and in the most difficult cases cause the death of the patient.
In addition, dilated vessels with thinner walls are at risk of mechanical damage that can cause serious bleeding.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of the disease are heaviness and fatigue in the legs, which usually appear in the evening and decrease when lying down.Veins take on a bluish tint and stand out on the surface of the skin, "spider veins" appear.(an enlarged network of capillaries visible through the skin), and a characteristic sign is that the venous pattern disappears if the limbs are raised higher (for example, placed in a chair).
Over time, varicose veins become more pronounced and appearthe appearance of small nodules or large conglomerates.
Unpleasant symptoms intensify and disturb patients even at night, they appearsoft tissue swellingmore often in the area of the legs, feet and ankles, as well as a feeling of fullness in the legs and cramps in the calf muscles.
In the absence of adequate treatment, varicose veins progressthe skin becomes dry, lumps and dark spots appear on it, and then trophic ulcers. With the development of thrombophlebitis, the veins become bright red, cord-like, and become painful when palpated.
When should you see a doctor?
Many people ignore the first signs of varicose veins, attributing it to ordinary fatigue. This greatly complicates the treatment of the disease and can lead to more serious consequences, thereforeYou should contact a phlebologist immediately after the symptoms of the disease appear.constant feeling of fatigue and heaviness in the legs, changes in the color of veins and skin, swelling, spider veins, etc.
Diagnosing
The diagnosis of "varicose veins of the lower extremities" is made after a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- general blood analysis- the number of red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes and hemoglobin level can be used to judge blood coagulation disorders and the presence of inflammation;
- ultrasonographyrepresents the most effective method for identifying affected vessels and vein sections;
- reovasographyit is performed to determine the lack of tissue nutrition with blood (the so-called rheographic index), on the basis of which the stage of the disease can be determined;
- phlebography, during which a contrast agent is injected into the veins, after which the condition of the venous system is assessed using an X-ray machine;
- physiological tests(Troyanov-Trendelenburg test, Hackenbruch test) make it possible to judge the functioning of the valve apparatus of the superficial veins.
Treatment
In the initial stages of varicose veins, it can be combated using conservative methods: taking medications, using ointments and gels, wearing compression garments and moderate physical activity. To correct cosmetic defects, patients may be recommended minimally invasive surgery or laser treatment. In the most advanced cases, varicose veins can only be eliminated through surgery, and its type is selected individually for each specific case.
Varicose veins of the legs are a disease whose occurrence is best prevented, because it is quite difficult to cure. Therefore, every woman should know the causes and signs of such a problem.
What are the dangers of varicose veins in the legs?
With the early development of the disease, many believe that its worst manifestation is the appearance of a swollen limb. Unfortunately, this is not the case. The worst case scenario for developing varicose veins in the legs in women is death. In addition, complications from the disease can be very different.
The most common are:
- trophic ulcers;
- thrombosis;
- phlebitis and thrombophlebitis.
Phlebitis is the process of damage to the inner walls of the vein. In this case, the leg swells more, and the elongated vessels become hard to palpation. With the further development of phlebitis, the patient's body temperature rises and every movement of the leg brings severe pain. And then phlebitis ceases to become thrombophlebitis. In this case, blood clots appear on the walls of the veins - small stagnant blood clots.
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in the absence of phlebitis. This problem is scary because it is almost impossible to diagnose.
Careful! A thrombus detached from the vessel wall is the cause of death in most clinical cases. Furthermore, this process occurs instantaneously (sometimes within minutes) and it is almost impossible to spot a detached blood clot before it stops the blood flow.
Now you know what are the causes of varicose veins in women's legs. To prevent varicose veins, it is necessary to constantly take preventive measures. This is especially true for those women who have a hereditary predisposition to the disease. To reduce the risk of the disease, it is necessary to have moderate physical activity, wear comfortable shoes and avoid hypotension.
Consequences and complications
There is no single course of varicose veins. Different groups of patients have individual characteristics of the disease course related to the pathogenesis of varicose veins. Varicose veins can be primary - that is, associated with congenital insufficiency of the venous valve and weakness of the vascular wall, which is almost always accompanied by reverse blood flow (reflux). And secondary (acquired), when reflux develops several years after the onset of the disease.
What are the dangers of varicose veins in women's legs? Varicose veins have a tendency to progress; with their development and in the absence of conservative treatment, the symptoms of the disease worsen. The heaviness in the legs is replaced by constant, continuous swelling, against the background of which tissue damage develops, open trophic ulcers appear, as a result of which the person completely loses his ability to work and requires constant maintenance therapy.
Treatment at home
Many women are interested in how to treat varicose veins on women's legs at home? Therapeutic exercises, herbal medicine and some recommendations for a healthy lifestyle for patients with varicose veins will help alleviate the symptoms of the disease and prevent its further development.
Therapeutic exercises
Every day in the morning and evening you should perform simple exercises for varicose veins:
- Lying on your back, raise your legs vertically, resting them on the wall at an angle of 90°. Hold this position for 3 minutes, breathing slowly through the chest, not the stomach.
- While lying on your back, do a cycling exercise for 3 – 5 minutes.
- While standing, raise both feet on the toes 1 cm from the floor and lower down. Perform 30 times in two approaches.
- While standing, alternately lift one heel off the floor, then the other, at an angle no higher than 45o. Start with 15 minutes a day, increasing to 30 minutes.
You should find time for a walk every day, at least 30 minutes. It is useful to go to the pool to swim once a week.
Folk remedies
Take the mixture of herbs from the inside: mix 1 tablespoon of birch buds, strawberry, string, calamus roots, mushroom leaves, thyme.
Pour boiling water over half a glass of the mixture and heat it in a water bath for 40 minutes. Let it cook, strain. Drink 0. 5 glasses before each meal for a month.
Make compresses from homemade ointments:
- Mix half a glass of curdled milk with chopped fresh wormwood leaves. Apply it to the diseased veins, secure with gauze on top and cover with film. Keep it for 30 minutes a day.
- Grate the beet on a fine grater, add 2 spoons of melted honey, mix, cool and apply to sore feet.
To eliminate evening swelling, apply fresh cabbage leaves to the ankle, first prick them with a fork until the juice appears. Secure it with a bandage.
Predictions and preventive measures
Since varicose veinsit is an irreversible process, there is no need to talk about complete recovery in this case. But with timely diagnosis, adequate treatment and prevention, patients can completely get rid of unpleasant symptoms and lead a full life.
Preventative measures for varicose veins includehealthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. People who are forced by their professional activities to stay in the same position for a long time are advised to avoid crossing the limbs, occasionally perform simple exercises, bend and straighten the legs and do a light massage forimprove blood circulation.
In your free time, you should take walks in the fresh air as often as possible and engage in moderate physical activity.
Ladies who follow fashion or work dress code and constantly go tohigh heels, you should change them from time to time for more comfortable shoes.
The same applies touncomfortable clothes, because even tight underwear can cause poor circulation and the appearance of varicose veins in women's legs.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities are today considered a widespread disease, which is often not given much importance.
It is very important to remember thatnot taking care of the health of your feet can cost a person not only his ability to work, but also his life, while in the initial stages, varicose veins can be corrected quite successfully using the simplest methods.

















